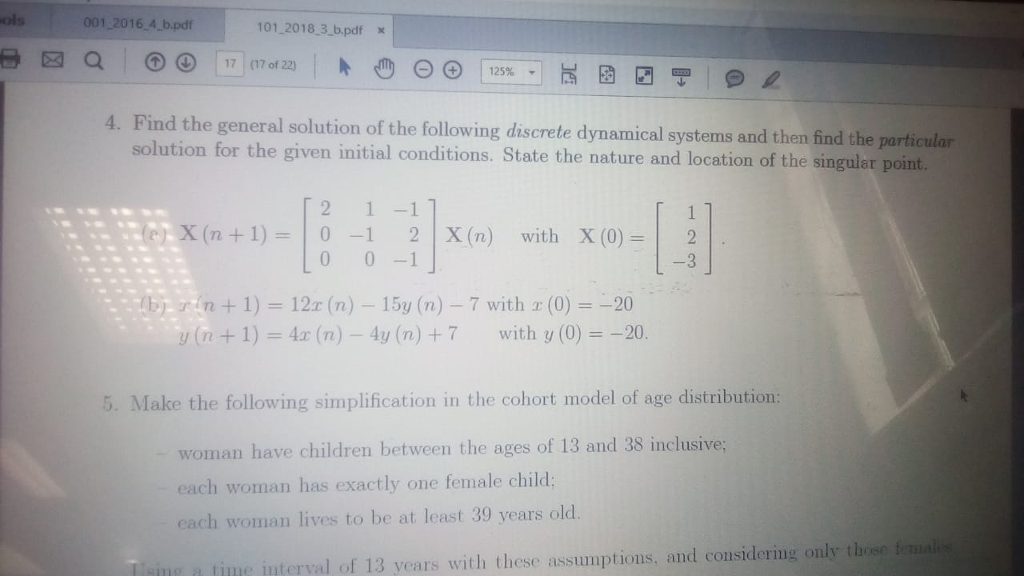
The volume features papers in difference equations and discrete dynamical systems with applications to mathematical sciences and, in particular, mathematical biology and economics. This book will appeal to researchers, scientists, and educators who work in the fields of difference equations, discrete dynamical systems, and their applications. Introduction to Discrete Dynamical Systems and Chaos makes these exciting and important ideas accessible to students and scientists by assuming, as a background, only the standard undergraduate training in calculus and linear algebra. Linear Dynamical Systems 1.1 System classifications and descriptions A system is a collection of elements that interacts with its environment via a set of input variables. The concepts of state vectors and divides the dynamical world into the discrete and the continuous. We then explore many instances of dynamical systems in the real world—our examples are drawn from physics, biology, economics, and numerical mathematics.Chapter 2 deals with linear systems. We begin with one-dimensional systems. Introduction to Discrete Dynamical Systems and Chaos makes these exciting and important ideas accessible to students and scientists by assuming, as a background, only the standard undergraduate training in calculus and linear algebra.
- Discrete Dynamical System Calculator
- A First Course In Discrete Dynamical Systems Pdf
- Discrete Dynamical Systems Pdf
The theory is illuminated by several examples and exercises, many of them taken from population dynamical studies. Solution methods of linear systems as well as solution methods of discrete optimization (control) problems are also included.
A timely, accessible introduction to the mathematics of chaos.The past three decades have seen dramatic developments in the theory of dynamical systems, particularly regarding the exploration of chaotic behavior. Complex patterns of even simple processes arising in biology, chemistry, physics, engineering, economics, and a host of other disciplines have been investigated, explained, and utilized.
 Introduction to Discrete Dynamical Systems and Chaos makes these exciting and important ideas accessible to students and scientists by assuming, as a background, only the standard undergraduate training in calculus and linear algebra. Chaos is introduced at the outset and is then incorporated as an integral part of the theory of discrete dynamical systems in one or more dimensions. Both phase space and parameter space analysis are developed with ample exercises, more than 100 figures, and important practical examples such as the dynamics of atmospheric changes and neural networks.
Introduction to Discrete Dynamical Systems and Chaos makes these exciting and important ideas accessible to students and scientists by assuming, as a background, only the standard undergraduate training in calculus and linear algebra. Chaos is introduced at the outset and is then incorporated as an integral part of the theory of discrete dynamical systems in one or more dimensions. Both phase space and parameter space analysis are developed with ample exercises, more than 100 figures, and important practical examples such as the dynamics of atmospheric changes and neural networks.An appendix provides readers with clear guidelines on how to use Mathematica to explore discrete dynamical systems numerically. Selected programs can also be downloaded from a Wiley ftp site (address in preface). Another appendix lists possible projects that can be assigned for classroom investigation. Based on the author's 1993 book, but boasting at least 60% new, revised, and updated material, the present Introduction to Discrete Dynamical Systems and Chaos is a unique and extremely useful resource for all scientists interested in this active and intensely studied field.
An Instructor's Manual presenting detailed solutions to all the problems in the book is available upon request from the Wiley editorial department. A timely, accessible introduction to the mathematics of chaos.
Discrete Dynamical System Calculator
The past three decades have seen dramatic developments in the theory of dynamical systems, particularly regarding the exploration of chaotic behavior. Complex patterns of even simple processes arising in biology, chemistry, physics, engineering, economics, and a host of other disciplines have been investigated, explained, and utilized.Introduction to Discrete Dynamical Systems and Chaos makes these exciting and important ideas accessible to students and scientists by assuming, as a background, only the standard undergraduate training in calculus and linear algebra. Chaos is introduced at the outset and is then incorporated as an integral part of the theory of discrete dynamical systems in one or more dimensions. Both phase space and parameter space analysis are developed with ample exercises, more than 100 figures, and important practical examples such as the dynamics of atmospheric changes and neural networks.